This website requires you to be 21 years or older to enter. Please confirm your age below to continue.
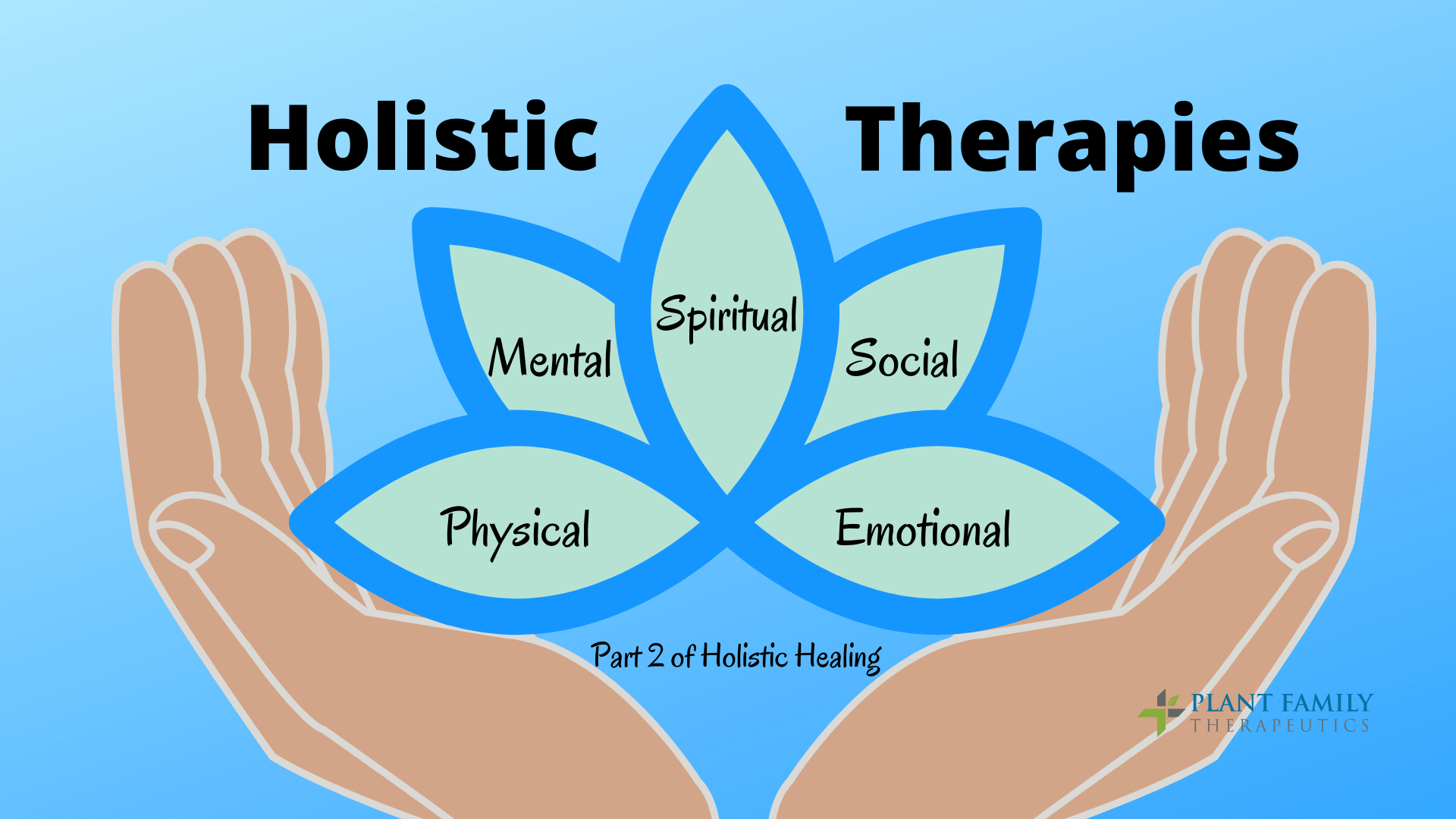
In this segment, part two of the holistic healing series, we will be taking a brief look into holistic healing treatments. The first segment, Rebuilding Pillars, invited you to investigate deep-rooted issues that may be preventing you from being your best self. Here you may find tools to help you in your journey to self-awareness and well-being.
Holistic Healing is the practice of health and wellness that considers the entire person and all of the internal and external factors affecting them.
What Is Holistic Healing?
The word holistic means “dealing with the whole.” Holistic healing involves the nurturing of the whole being, including their mind, body, and spirit (the emotional, mental, and even spiritual aspects that affect the condition). Holistic healing seeks to maintain and restore balance among (and within) the various dimensions of the individual, rather than focusing only on the physical ailment or condition.
Holistic health is an approach to life. It is living in ways that emphasize the interconnected nature of the mind, body, and spirit. It is the belief that our health and wellness are a result of all parts of who we are, as well as how we interact with our surroundings. Holistic health means we take responsibility for our own well-being. As such, it is the outcome of all the choices and actions you take daily.
Ancient Roots of Holistic Healing
Holistic healing may be a new way of thinking in westernized medicine, but it’s not a new concept. Holistic healing is an ancient practice and the origin of all medicine which has evolved as a result of our growth as people.
The principles of holistic healing can be summarized into three properties: the whole person, natural elements, and personal empowerment. Ancient thinkers and healers recognized the importance of these perspectives thousands of years ago.
During the 4th century B.C. Socrates advised that treating one area of the body would not have the same positive effects as treating the whole body. Even Hippocrates, the father of modern medicine, encouraged self-healing of the body and emphasized the healing power of nature in his Hippocratic School of Medicine. In India during the 6th century B.C., Ayurveda, a form of herbal medicine that focuses on healing the energies within the body using the medicinal properties of plants, started and is still practiced today.
Hildegard of Bingen was a practitioner and pioneer of traditional German herbal medicine during medieval times. Her work was so significant a branch of her traditional work known as Hildegard Medicine is practiced today. Traditional Chinese medicine has been around for almost 5,000 years and has influenced medicine around the world.
“…the part can never be well unless the whole is well.” – Socrates
It was the discovery of germs and their role in the cause of disease that moved doctors away from holistic healing and into a practice of focused treatment. Most diseases and illnesses could be treated by medicines such as penicillin. The holistic view of the patient became a secondary consideration, if at all. As a result, physicians paid less attention to the whole patient. Instead, they focused on improving the various interventions to deliver drugs and to remove or repair damaged parts. Patients were alienated from their own health care and began to rely on medicine to “fix” them.
Interestingly, in the 1960s, a shift started as people began to move away from modern drugs and medical technology and push for more natural healing methods. In 1975 the National Conference on Holistic Health was held in California, and just three years later, the Holistic Medical Association came into being. Today, holistic practitioners must go through rigorous training similar to that of a medical doctor, but with a focus on herbal therapies, environmental problems, and nutrition in addition to conventional medication.
Common Principles of Holistic Treatment
There are several guiding principles central to holistic medicine and treatment, including:
These principles help practitioners work with patients to choose therapies that promote better overall health: mind, body, and spirit.
Types of Holistic Treatments
Each holistic practitioner will have his or her own chosen path to wellness, but there are several example treatments common to holistic practices. Below are very brief descriptions of some treatments used:
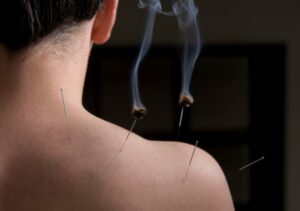
Acupuncture uses needles to stimulate areas of the body to release energy or activate the nervous system to help ease chronic conditions. Moxa is a form of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that involves burning herbs like cannabis over the body or via acupuncture needles. Acupressure does the same thing, but instead of needles, it uses a small amount of pressure.
Aromatherapy uses the sense of smell to help calm the body and soothe some ailments. Want to give your cannabis a boost? Try aromatherapy! That’s right, burn lemon or citrus essential oils to enhance happiness or try lavender for better sleep and less anxiety.
The Ayurvedic practice uses herbs, including cannabis, and dietary changes to address health issues. It’s based on the belief that health and wellness depend on a delicate balance between the mind, body, and spirit. This practice also focuses on how people and their environments are closely connected.
Chiropractic care uses gentle manipulation of the spine and neck to improve the body’s function by improving the function of the nervous system. This can help support the treatment of physical and muscular pain, headaches, or even illness.
Osteopathy is similar to chiropractic care but involves more than the spine; it covers the whole body. An osteopath can manipulate the entire musculoskeletal system to help improve the function of the muscles and nerves and support a strong, healthy bone structure.
Naturopathy uses natural treatments, including herbs and dietary supplements, to support overall health. A naturopathic practitioner may also encourage exercise and dietary changes to help patients feel better.
Loosening tight muscles and tissues with massage therapy can support overall health and wellness. Many holistic practitioners will use massage in their treatments. Many therapists are using CBD oil along with their massage oil for an extra boost of healing power.
Wellness covers the whole body, and that includes proper nutrition. Individuals learn which foods work best for their specific condition. Did you know, like aromatherapy, compounds in the foods you eat can enhance the healing power found in cannabis?

Because holistic medicine takes a mind-body-spirit approach to healing, it often involves mental health therapy. When a person is equipped to manage stress and deal with mental health needs in a healthy manner, they are better equipped to heal.
Yoga is more than just a form of exercise. It helps with the mind-body connection and creates calmness in the spirit. This supports the holistic view of overall wellness.
Energy healing is a holistic practice that activates the body’s subtle energy systems to remove blocks. By breaking through these energetic blocks, the body’s inherent ability to heal itself is stimulated.
Holistic Vs. Conventional Medicine
If you visit a traditional doctor with an ailment or concern, the doctor will provide medical solutions to take care of your symptoms. These might include procedures or medications. If possible, the solutions will eradicate the disease and the germs that cause it.
A holistic practitioner will dig deeper to find the cause of the disease or its symptoms. They will then use multiple types of therapies, often in conjunction with traditional medical practices, to treat not only the symptoms, but also their cause. In addition to prescription medication, they might encourage lifestyle changes and dietary changes that would help prevent the issue from returning.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Holistic Medicine
Pros of Holistic Medicine
A holistic approach to patient care and wellness has several benefits, including:

Cons of Holistic Medicine
Like all treatment methods, holistic care does have a few drawbacks:
Looking Forward
The ancient properties of holistic healing are slowly making their way back into conventional medicine. Still, the acceptance of holistic healing within the medical community has been slow. This will likely continue, but holistic healing is making progress. Medical practitioners are recognizing that holistic healing offers both immediate and long-term benefits that need to be explored.
References
Agarwal, V. (2018). Complementary and alternative medicine provider knowledge discourse on holistic health. Front. Commun. 3:15 https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomm.2018.00015
Demirsoy, N. (2017). Holistic care philosophy for patient‐centered approaches and spirituality. Patient Centered Medicine. IntechO pen. https://doi.org/10.5772/66165
King, H. (2020). Treating the patient, not just the disease: Reading ancient medicine in modern holistic medicine. In: Thumiger, C ed. Leiden: Brill, pp. 402-426 https://brill.com/view/title/58241
Pan, S. Y., Litscher, G., Gao, S. H., Zhou, S. F., Yu, Z. L., Chen, H. Q., Zhang, S. F., Tang, M. K., Sun, J. N., & Ko, K. M. (2014). Historical perspective of traditional indigenous medical practices: The current renaissance and conservation of herbal resources. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2014, 525340. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/525340
Tabish S. A. (2008). Complementary and Alternative Healthcare: Is it Evidence-based?. International journal of health sciences, 2(1), V–IX. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068720/#!po=78.1250
Yuan, B. (2019). Toward holistic medicine and holistic biology: Life sciences after precision medicine and system biology. Frontiers in life science, 2019. 12 (1), 14-26. https://doi.org/10.1080/21553769.2019.1682064